In my last piece, I talked about Web3 and how the future of the internet is shaping around it. As we look ahead towards a decentralized future it is important to understand how will companies and organizations shape up in the decentralized world. DAO or decentralized autonomous organization is changing how organizations function and for good. The idea is to have no central authority and hierarchy in simple terms it’s an internet community where every stakeholder has a seat on the table, there is transparency and the incentives are maximized. In this piece, I will go a little deeper into the DAO, how it functions and how it’s not just your regular company on blockchain. Dive in!
What is DAO
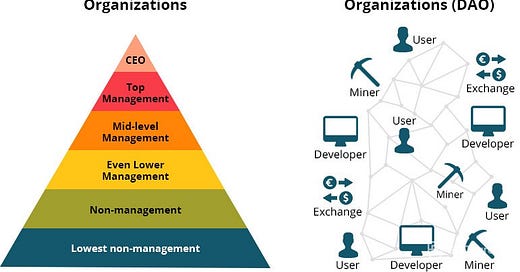
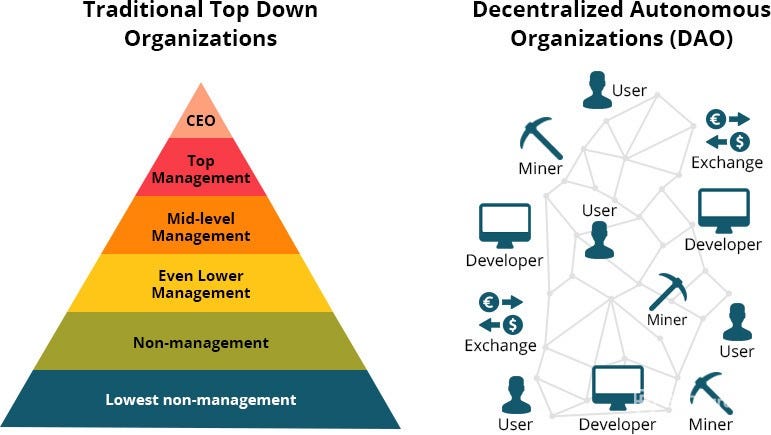
Decentralized autonomous organizations are entities that operate through smart contracts. Its financial transactions and rules are encoded on a blockchain, effectively removing the need for a central governing authority.
Decentralized = Online, global, uncensorable.
Autonomous = Self-governing.
Organization = Coordination & collaboration around shared objectives.
Think of them like an internet-native business that's collectively owned and managed by its members. They have built-in treasuries that no one has the authority to access without the approval of the group. Decisions are governed by proposals and voting to ensure everyone in the organization has a voice.
DAOs solve for the age-old principle-agent dilemma, in simpler terms it is when the agent of an organization has the power to make decisions on behalf of, or impacting, the principal (another person or entity in the organization). Like Executives making decisions on the behalf of shareholders, politicians on behalf of citizens. This is solved by the DAO where stakeholders cumulatively make a decision without any intermediary, Its like a perfect cooperative.
How does a DAO work:
A group of people writes the smart contracts (programs) that will run the organization
There is an initial funding period, in which people add funds to the DAO by purchasing tokens that represent ownership – this is called a crowd sale, or an initial coin offering (ICO) – to give it the resources it needs.
When the funding period is over, the DAO begins to operate.
People then can make proposals to the DAO on how to spend the money, and the members who have bought in can vote to approve these proposals.
History of DAO
DAO is one of the most popular and successful implementations on the blockchain technology. It started in 2016 when a group of developers from the Ethereum community came together to build an investor directed venture capital fund also known as the Genesis DAO. Anyone could join the DAO by sending ether to the DAO smart contract, the platform allowed anyone to pitch their idea to the community and receive funding if approved. Within a few weeks of launch the DAO raised more than $150M one of the largest crowdfundings in history, it was an instant hit.
The euphoria was cut short pretty soon as the algorithms were vulnerable and an attack started depleting the funds, the DAO token value dropped, ether’s value went down by a third, investors saw their money vanish in real-time, however, the damage was recovered just in time as the community acted quickly and used a hardfork method to retransfer the funds before the hacker could encash them, the heist was averted, despite this concerns on the DAO started growing and the young ethereum had some work to do to maintain security and prevent bad actors from ruining the system.
“The bug that was exploited by the hacker was, appropriately enough, found on line 666 of the smart contract code of The DAO. It was later determined that if a capital T in a command on that line had been lowercase, the theft would not have been possible.” - “The story of blockchain” by Omid Malekan
United States Securities and Exchange Commision (SEC) in a ruling in 2017 put DAO tokens into the securities category and stated that they were subject to the same laws as any company going for a Initial public offering (IPO), this made blockchain startups and developers come up with ways to avoid regulation.
Though the DAO has a rough start it was one of the paramount use cases f the blockchain and has been growing ever since, the hack was an eye opener on the need for security but as we speak today there is no word more buzzier than DAO.
Conclusion
The DAO is basically a group of people who come together in an internet community for a common goal, individual contributors on the available bounties and the top few who show the proof of work are rewarded, everything is trasparanent with the only governing body being the code, yes you can say DAO is basically a code, but there is lot to it than that. Why are getting so popular because it maximizes the incentives and gives everyone no matter where you are, which background you are from, your degree, nationality, gender etc a seat at the table and equal incentives.
DAO is like a party, vibe matters - vibe is the fuel.
Explaining DAOs taking Amul as an example: (Credits - Osborne Saldanha - Fintech Inside)