If you are reading this, you are a participant of the web. It's amazing how I can publish content and you can read it without actually writing a single line of code or operating a server. The evolution of the web from 1 to 2 to now 3 has been phenomenal. There has been a lot of buzz around Web3 and its implications. I get tweet floods each day on web3 and it seems to be some kind of utopian decentralized future the web is looking towards. In this piece, I will walk you through What web 3 is, how will it solve for the issues with web 2, what to expect, and give you a sense of understanding of how the future of the internet looks like.
The Evolution of Web
The journey started in 1989 when Tim Berners Lee wrote his seminal document “ Information Management: A proposal. He proposed the theory of the web as a network of information systems interconnected via hypertext links and participants will be able to access the network in a decentralized manner through remote machines and systems allowing them to be linked together without requiring any central control or coordination.
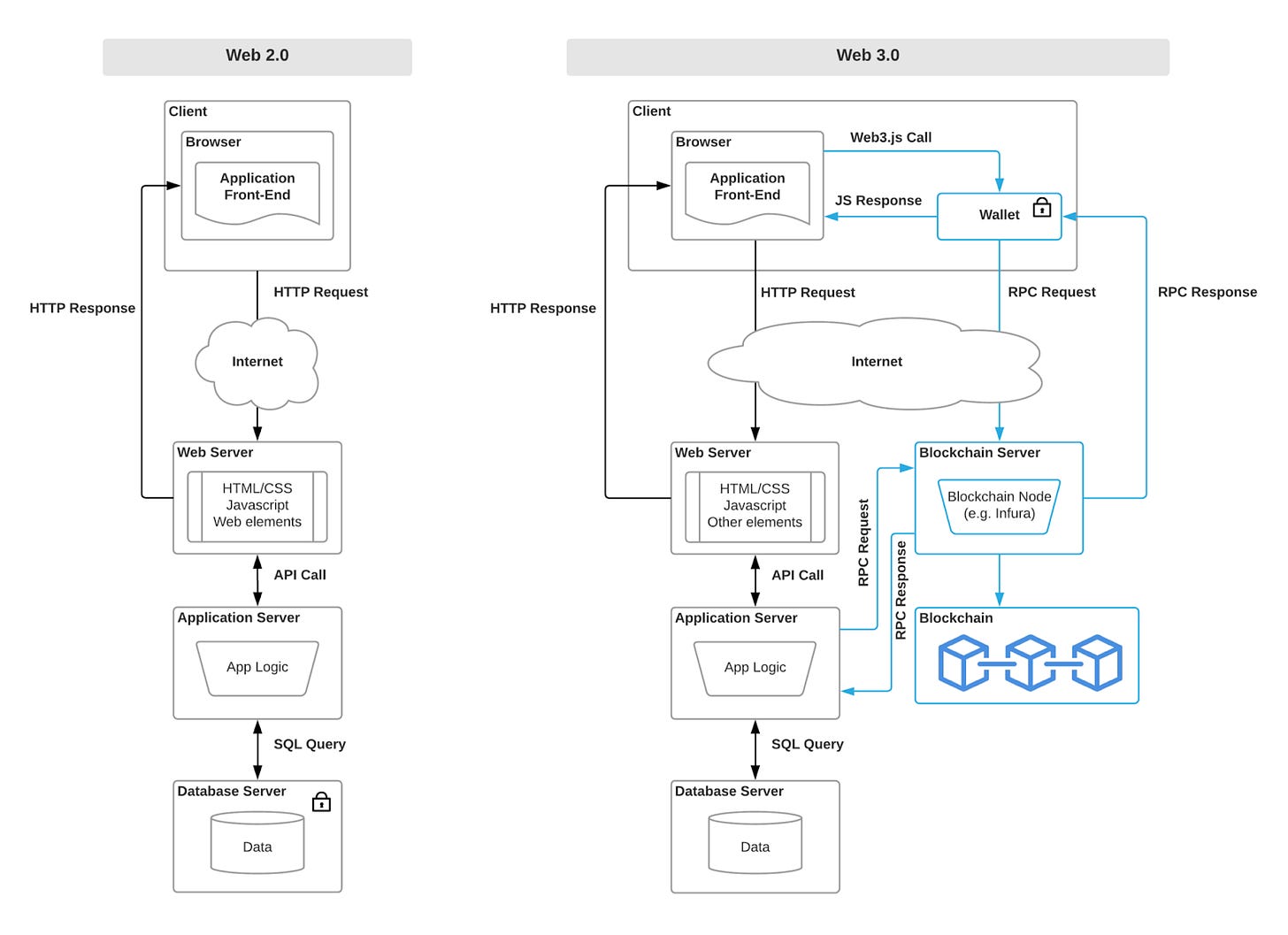
This materialized into web1, A static set of interconnected resources accessed via a distributed set of servers on a read-only basis from the client. Web 1 lasted till the early 2000s. Here organizations could build their internet presence without worrying about the change of rules. A good chunk of today’s internet behemoths like yahoo, google, amazon, Facebook were started during web1.0. As the years progressed these tech companies built software and services that rapidly outpaced the capabilities of open protocols. The penetration of smartphones increased and mobile apps contributed to the majority of internet use. Eventually, we progressed from open protocols to a much-centralized web we know today web 2.0.
Web2 was a boon in terms of giving people access to technologies, many of which are free to use. What changed:
Web browsers became mainstream and paved the way for content discovering services like search engine
Network effects that were driven earlier by hyperlinks were scaled by platforms that enabled user engagement through the collective information gathered.
Data became a valuable commodity.
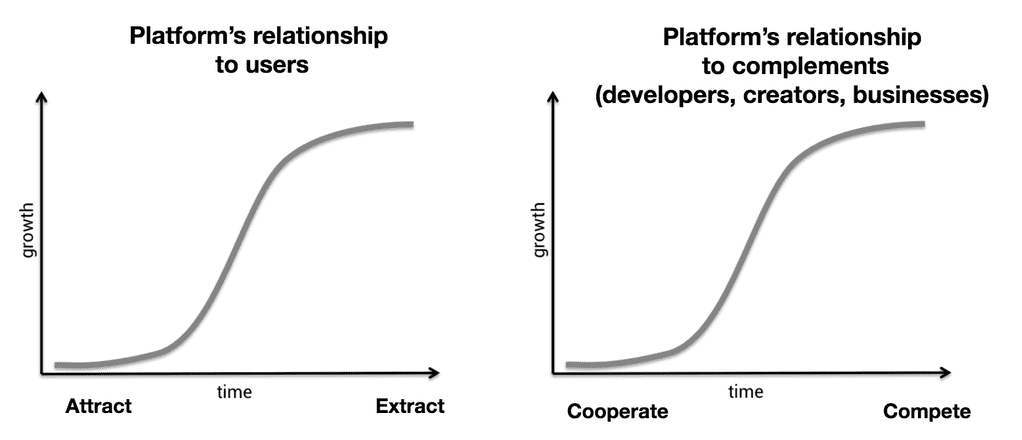
However, this stifled innovation as it became much harder for organizations and creators to grow their online presence without worrying about centralized platforms changing the rules taking away their audiences and profits. Web 2 lacks independent trusted operators and it is controlled by software providers. The success of web2 stressed on the point that it is difficult to build a decentralized platform at scale.
Bitcoin was built on a peer 2 peer distributed ledger blockchain where you can transact tamper-proof. This was a breakthrough in decentralized technology, following which a lot of use cases were built on blockchain. Bitcoin runs billions worth of transactions on its distributed nodes it day and drives home the point that a decentralized ecosystem can be built on scale.
Decentralization enables the data to be held by the participants instead of a single party for instance lets take my blog, today I publish it on substack or medium or a social platform like Twitter and if these companies decide to shut me off for some reason I lose all my viewers and subscribers and content on the other hand if i use a decentralized ecosystem my content can be hosted on multiple locations across multiple entities and outrage from one node will not make it disappear.
With bitcoin, each participant in the web can now hold and trade digitally, many people started building on the blockchain layer and with the advent of ethereum it became more and more easier. Being bullied by the centralized ecosystem, people started looking for decentralized alternatives and Web3 came into the picture.
What is Web3
Web3 is the internet owned by builders and users and facilitated by crypto tokens. It is a cluster of decentralized apps that run on the blockchain, these apps allow anyone to participate without using their personal data to pay for it.
Benefits of Web3
No permission is required, anyone on the network can access and publish content.
No one can block anyone or restrict access.
Payment apps are built on crypto and require no personal data, neither can they prevent payments.
Limitations of web3
Scalability is an issue that is getting figured out by networks like polygon(can read about it in my previous piece) as of now transactions on Web3 are slower as they are decentralized and it needs to be processed by a miner and propagated to the network.
Web3 is not integrated with web browsers thus creating an issue of accessibility
It’s not user-friendly and to interact with web3 apps one should have an understanding of the software.
Conclusion
The Internet today is used by 4.7 Bn people. The web has come a long way from static Web1 to a widely used Web2 to now developing Web3. Web3 is challenging web2's centralized approach which reached the masses with distributed networks built on open protocols vesting the power in the hands of the users rather than a centralized corporation. Web3 is a user-controlled internet and is a step towards further evolution, how it will play out and how will it affect us in something for time to tell, as we speak it is still in very nascent stages and too early to predict however I am very optimistic about it, it is about time to democratize the Web.
Sources: web3 foundation, coinbase, patrick macormick, twitter, ethereum org, The news stack, cris dixon.